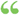 Spherical Triangle the cosine of any side is equal to the product of the cosines of the other two sides, plus the product of the sines of those sides into the cosine of their included angle ; that is, (1) cos a = cos b... Spherical Triangle the cosine of any side is equal to the product of the cosines of the other two sides, plus the product of the sines of those sides into the cosine of their included angle ; that is, (1) cos a = cos b...  Trigonometry - Page 113by Alfred Monroe Kenyon, Louis Ingold - 1913 - 256 pagesFull view Trigonometry - Page 113by Alfred Monroe Kenyon, Louis Ingold - 1913 - 256 pagesFull view - About this book
 | Daniel Cresswell - Geometry - 1816 - 352 pages
...from the other complemental triangle. PROP. I. (230.) Theorem. The cosine of any one of the sides, of a spherical triangle, is equal to the product of the cosines of the other two sides, together with the continued product of the sines of those two sides, and the cosine of the angle contained... | |
 | Anthony Dumond Stanley - Geometry - 1848 - 134 pages
...spherical triangles. In the form of a theorem it may be stated thus : The cosine of one of the sides of a spherical triangle^ is equal to the product of the cosines of the other two sides, increased by the product of their sines multiplied into the cosine of the included angle. There are... | |
 | William Chauvenet - 1852 - 268 pages
...the various positions of the lines of the diagram. 5. In a spherical triangle, the cosine of any side is equal to the product of the cosines of the other two sides, plus the continued product of the sines of those sides and the cosine of the included angle. Let the plane B'A'С',... | |
 | Adrien Marie Legendre - Geometry - 1852 - 436 pages
...sin a sin c cos B, L (1) cos c = cos a cos b + sin a sin b cos (7. J That is : The cosine of either side of a spherical triangle is equal to the product of the cosines of the two other sides plus the product of their sines into the cosine of their included angle, enter into... | |
 | Horatio Nelson Robinson - Geometry - 1860 - 470 pages
...gives cos.ACD = cot. AC cos.BCD cot.BC Or, cot. AC : cot.BC = cos. ACD : cos.BCD. PROPOSITION VII. The cosine of any side of a spherical triangle, is...two sides, plus the product of the sines of those sides multiplied by the cosine of the included angle. Let ABC be a spherical triangle, and CD a perpendicular... | |
 | Benjamin Greenleaf - Geometry - 1862 - 518 pages
...the sine of C. (147) (148) (149) TRIGONOMETRY. 149. In any spherical triangle, the cosine of any side is equal to the product of the cosines of the other...two sides into the cosine of their included angle. Let A BC be any spherical triangle, 0 the centre of the sphere. Draw the plane B' A' C' perpendicular... | |
 | Benjamin Greenleaf - Geometry - 1862 - 532 pages
...of B1 Ö D is still equal to the sine of G. 149. In any spherical triangle, the cosine of any side is equal to the product of the cosines of the other...two sides into the cosine of their included angle. Let ABC be any spherical triangle, O the centre of the sphere. Draw the plane B1 A1 O perpendicular... | |
 | John Mulcahy - Geometry - 1862 - 252 pages
...circles whose poles are the extremities of the base. Since the cosine of the hypotenuse of a right-angled spherical triangle is equal to the product of the cosines of the sides, the locus of the vertex of such a triangle, whose hypotenuse is given, is a spherical ellipse.... | |
 | Benjamin Greenleaf - Geometry - 1863 - 504 pages
...«till equal to the sine of C. 7* TRIUONOMETRY. 1 49. In any spherical triangle, the cosine of any side is equal to the product of the cosines of the other...two sides into the cosine of their included angle. Let ABC be any spherical triangle, 0 the centre of the sphere. Draw the plane B1 A' O perpendicular... | |
 | Benjamin Greenleaf - 1867 - 188 pages
...In like manner, by means of (153), sinJB = ^°3^. (197) cos p ^ 161. T^e cosine of the hypothenuse is equal to the product of the cosines of the other two sides. By means of (152) we have cos A = cos p cos b -\- sin p sin b cos C, which, by making O = 90°, becomes... | |
| |